SEC595: Applied Data Science and AI/Machine Learning for Cybersecurity Professionals


Experience SANS training through course previews.
Learn MoreLet us help.
Contact usBecome a member for instant access to our free resources.
Sign UpWe're here to help.
Contact UsLearn how to amplify and improve your human risk management program using AI

Note: This blog post is the first in a series on what Artificial Intelligence (AI) is, the different types and how they work, the legal / security issues potentially involved, and most importantly how to make the most of it as part of you Security Awareness / Human Risk efforts. This series will provide a broad overview of AI but then later in the series focus primarily on what is known as Generative AI. The goal of these posts is to not only amplify and improve the maturity of your program, but also provide you the skills to grow your reputation and career. You can access the other blog posts from this series below.
AI are systems programmed to think and respond like humans. In fact, I asked the AI system ChatGPT that very question. This was its response:
“Artificial intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think and learn like humans. It involves the development of algorithms and computer programs that can perform tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as recognizing speech, understanding natural language, making decisions, and playing games. There are several types of AI, including rule-based, expert systems, and machine learning.”
What makes AI so powerful is that it can have the intelligence and reasoning capability of the human mind but can analyze exponentially more information and do it in a matter of seconds. The concept of AI is not new. Originally covered in science fiction novels, AI has been in development for decades. We are hearing so much about it now because for the first time, we have the chance to interact with and see the true functionality of AI.
ChatGPT, an online-powered AI chat bot, is one of the first publicly available chat bots that has the ability to think and respond like a real human, passing what’s called the Turing Test. Originally developed by Alan Turing in 1950, the Turing Test determines a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior by having a real human interact and have a conversation with the machine via a test-based chat channel. If the human cannot tell whether they are interacting with a machine or a person (in other words, they cannot tell the difference), the machine passes the test.
Learn more about SANS Institute’s SEC595: Applied Data Science and AI/Machine Learning for Cybersecurity Professionals and sign up for a FREE course preview here. |
ChatGPT and other AI solutions today are some of the first publicly available solutions that do just that. However, online conversations are just the beginning of what AI can do. There are now AI solutions that can create in real-time a video of a real person teaching anything you want in any language you want, analyze millions of health records and quickly determine who most likely has cancer, create news articles or essays on the topic of your choice, generate images for children’s books or analyze and understand images you submit, and generate code for new computer programs.
AI is not to be feared, it is simply a very new and powerful tool that we can take tremendous advantage of. One of the biggest challenges we face in cybersecurity, especially when trying to address human risk, is the teams responsible are often grossly understaffed lacking the people and resources to effectively get the job done. AI has the ability to exponentially increase your capacity and amplify your impact at a fraction of the time and cost of traditional methods. As such I’ll be going into the numerous ways and examples of how you can safely and securely leverage AI.
AI describes a very large and diverse field of research. There are many terms used to define AI and related sub-fields, so it can get very confusing very fast. Below, I simplify key elements of AI and how they relate to each other. Remember, I’m focusing on the use of AI from a managing human risk perspective, so what I cover here is only a small part of a very broad science.
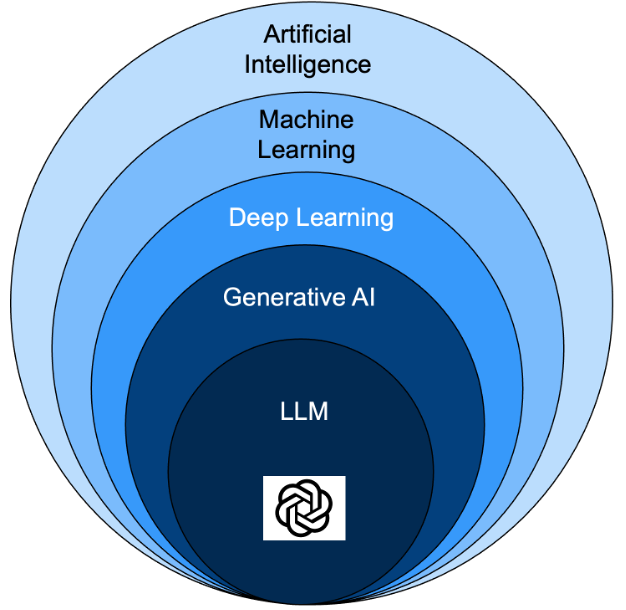
As you begin to better understand AI you can also understand both the advantages and disadvantages of AI. The advantage is its ability to quickly analyze huge amounts of data (as in billions of data points), identify patterns and leverage those patterns. The disadvantage of AI is the answers or output is only as good as the data it has analyzed and it is only as good as the algorithms used to analyze that data, to include any human biases that have been introduced into those algorithms.
Interested in reducing your organization’s human risk? Check out my course LDR433: Managing Human Risk and sign up for a FREE course preview here.
In part two of this series, we go into details of what generative AI is and how to leverage it using a method called prompt engineering. If you have a specific question about leveraging AI that you would like me to cover, please reach out at lspitzner@sans.org.


Lance revolutionized cyber defense by founding the Honeynet Project. At SANS, he has empowered over 350 organizations worldwide to build resilient security cultures, transforming human risk management into a cornerstone of modern cybersecurity.
Read more about Lance Spitzner