SEC595: Applied Data Science and AI/Machine Learning for Cybersecurity Professionals


Experience SANS training through course previews.
Learn MoreLet us help.
Contact usBecome a member for instant access to our free resources.
Sign UpWe're here to help.
Contact UsShape your awareness program with trusted risk-driven security awareness training that redefines human risk management and ultimately drives a strong security culture.

We combine expert-led, role-specific security awareness training with strategic resources to build and grow effective security awareness programs. From assessing your culture and knowledge gaps to delivering targeted phishing simulations, our approach is grounded in real-world impact. Backed by the industry-leading Security Awareness Report, the proven Maturity Model, and insights shared at the annual Security Awareness Summit, SANS provides the tools and thought leadership you need to shape a security-first culture—and prove it’s working.
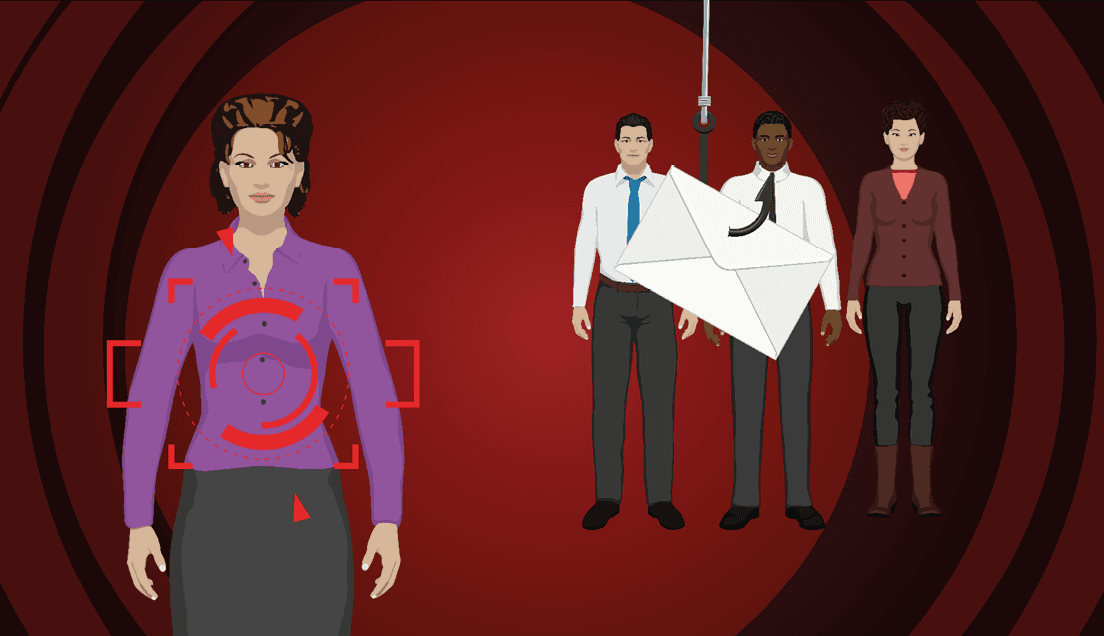
Proven results with real-world phishing simulation. Keep your employees at the highest level of security awareness through continuous training and testing. The platform allows you to control every aspect of your phishing awareness program, with pre-configured or customizable phishing tests, just-in-time training, and automated remedial courses.
A library of over 50 training modules across 6 tracks, curated by SANS Subject Matter Experts to reduce risk, increase awareness and mature programs. Translated into over 34 languages and delivered in engaging formats to meet the needs of every learner at your organization.

Establish a baseline and measure progress over time with assessments that reveal gaps in behavior, mindset, and understanding — helping you target efforts where they matter most.

SANS industry leading report gives you access to benchmark data, expert insights, and actionable recommendations drawn from thousands of Security Awareness Officers, and their programs worldwide, so you know what works, what doesn’t, and why.

Use the proven SANS Security Awareness & Culture Maturity Model to build and evolve your awareness program in stages, with clear guidance on how to move from compliance-focused to long-term, sustainable culture change, and metrics to benchmark your progress.

Discover how SANS can help you create lasting, behavior-driven changes across your workforce.
Contact Us Today